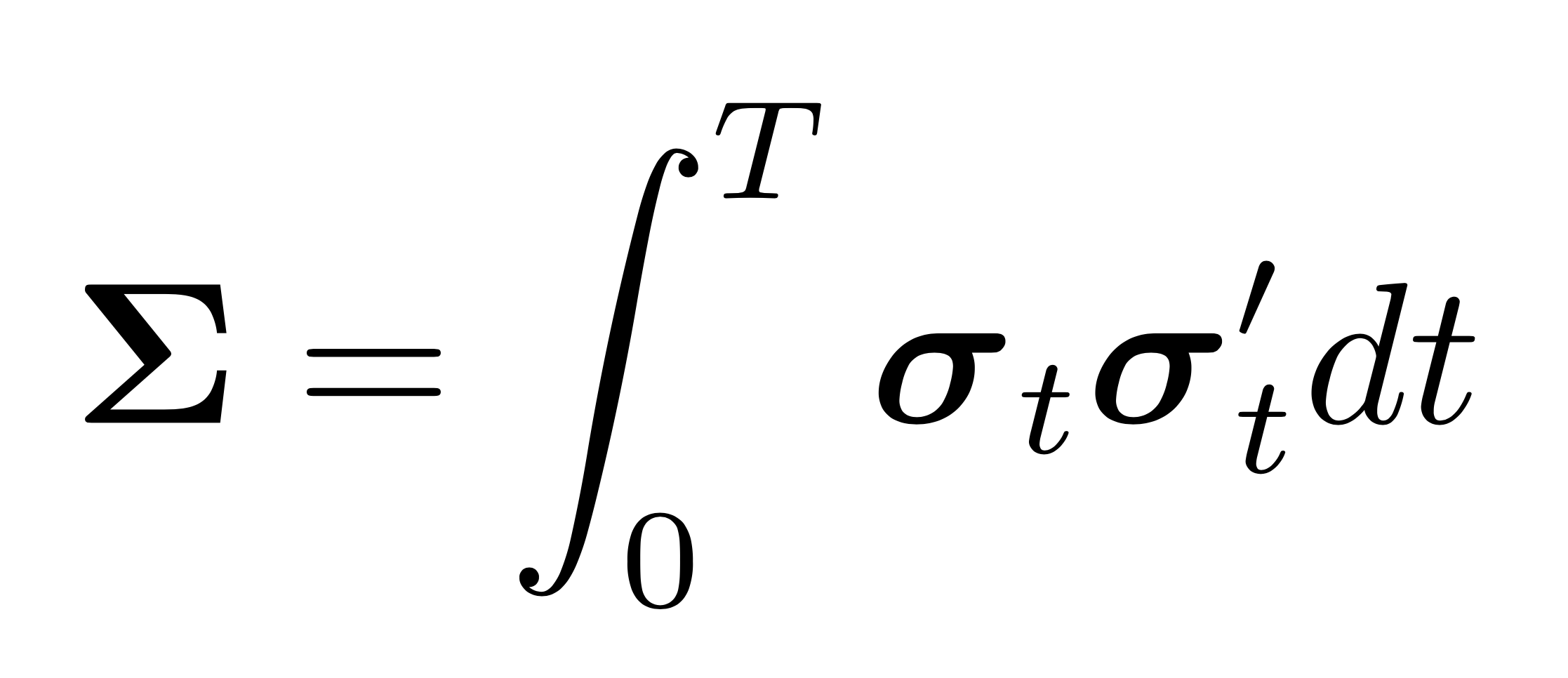import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import numba
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.animation as animation
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from hfhd import hd
[docs]@numba.njit
def garch_11(n, sigma_sq_0, mu, alpha, beta, omega):
r"""
Generate GARCH(1, 1) log-returns of size n.
This function is accelerated via JIT with Numba.
Parameters
----------
n : int
The length of the wished time series.
sigma_sq_0 : float > 0
The variance starting value.
mu : float:
The drift of log-returns.
alpha : float >= 0
The volatility shock parameter. A higher value will lead to
larger spikes in volatility. A.k.a short-term persistence.
beta : float >= 0
The volatility persistence parameter. A larger value will
result in stronger persistence. A.k.a long-term persistence.
omega : float > 0
The variance constant. A higher value results in a higher
mean variance.
Returns
-------
r : numpy.ndarray
The GARCH log-returns time series.
sigma_sq : numpy.ndarray
The resulting variance time series with which each log-return
was generated.
Notes
-----
In general, the conditional variance of a GARCH(p,q) model is given by
.. math:: \sigma_{t}^{2}=\omega+\sum_{i=1}^{q} \alpha_{i}
\varepsilon_{t-i}^{2}+\sum_{j=1}^{p} \beta_{j} \sigma_{t-j}^{2}.
The unconditional variance is given by
.. math:: \sigma^{2}=\frac{\omega}{1-\sum_{i=1}^{q}
\alpha_{i}-\sum_{j=1}^{p} \beta_{j}}.
Here, :math:`p=q=1`,
and :math:`\epsilon_{t} \sim \mathcal{N}\left(0, 1\right)`
"""
nu = np.random.normal(0, 1, n)
r = np.zeros(n)
epsilon = np.zeros(n)
sigma_sq = np.zeros(n)
sigma_sq[0] = sigma_sq_0
if min(alpha, beta) < 0:
raise ValueError('alpha, beta need to be non-negative')
if omega <= 0:
raise ValueError('omega needs to be positive')
if alpha+beta >= 1:
print('''alpha+beta>=1, variance not defined
--> time series will not be weakly stationary''')
for i in range(n):
if i > 0:
sigma_sq[i] = omega + alpha * epsilon[i-1]**2 + beta * sigma_sq[i-1]
epsilon[i] = (sigma_sq[i]**0.5) * nu[i]
r[i] = mu + epsilon[i]
return r, sigma_sq
[docs]class Universe:
r"""
The universe is a specification from which simulated realizations
can be sampled. Stocks follow a factor model, they belong
to industries and have an idiosyncratic component. Stocks are predictable
by a single feature.
Attributes
----------
feature_beta : float
The true coefficient.
factor_garch_spec : list
The garch specification for factor returns.
``[sigma_sq_0, mu, alpha, beta, omega]``
industry_garch_spec : list
The garch specification for industry returns.
``[sigma_sq_0, mu, alpha, beta, omega]``
resid_garch_spec : list
The garch specification for residual returns.
``[sigma_sq_0, mu, alpha, beta, omega]``
factor_loadings : numpy.ndarray
An array with factor loadings for each stock and factor.
dim = n_stocks x n_factors
industry_loadings : numpy.ndarray
An array with industry loadings for each stock and industry.
dim = n_stocks x n_industry
This is usually a sparse matrix. One stock loads typically on
one or two industries. A good number of industries is 10 to 20.
liquidity : float
A value between 0 and 1 that describes liquidity.
A value of 1 means that the probability of observation
is 100% each minute. 0.5 means that there is a 50%
probability of observing a price each minute.
gamma : float >=0
The microstructure noise will be zero-mean Gaussian with variance
$\gamma^2 var(r)$, where $var(r)$ is the variance of the
underlying true return process. This noise is be added to the price.
freq : str, ``'s'`` or ``'m'``.
The granularity of the discretized continous price process.
"""
def __init__(self, feature_beta, factor_garch_spec, industry_garch_spec,
resid_garch_spec, factor_loadings, industry_loadings,
liquidity=0.5, gamma=2, freq='m'):
self.feature_beta = feature_beta
self.factor_garch_spec = factor_garch_spec
self.industry_garch_spec = industry_garch_spec
self.resid_garch_spec = resid_garch_spec
self.factor_loadings = factor_loadings
self.industry_loadings = industry_loadings
self.liquidity = liquidity
self.gamma = gamma
self.freq = freq
self.n_stocks = self.factor_loadings.shape[0]
self.n_ind = self.industry_loadings.shape[1]
self.n_factors = self.factor_loadings.shape[1]
[docs] @staticmethod
def uncond_var(spec):
'''
Compute the uncoditional variance from a
GARCH(1,1) specification.
Parameters
----------
spec : list
The garch specification.
``[sigma_sq_0, mu, alpha, beta, omega]``
Returns
-------
float
The unconditional variance.
'''
return spec[4]/(1-spec[2]-spec[3])
[docs] def uncond_cov(self):
'''
Compute the uncoditional covariance of stock returns
in the universe from a universe specification.
Returns
-------
numpy.ndarray
The unconditional covariance matrix.
'''
sf = np.diag([self.uncond_var(self.factor_garch_spec)]*self.n_factors)
sr = np.diag([self.uncond_var(self.resid_garch_spec)]*self.n_stocks)
si = np.diag([self.uncond_var(self.industry_garch_spec)]*self.n_ind)
return (self.factor_loadings @ sf @ self.factor_loadings.T
+ sr
+ self.industry_loadings @ si @ self.industry_loadings.T)
[docs] def cond_cov(self):
'''
Compute the daily coditional integrated covariance matrix of stock
returns within regular market hours in the universe from a realized
universe simulation.
Returns
-------
list
A list containing the conditional integrated covariance matrices
of each day.
'''
sr = pd.DataFrame(self.sigma_sq_resid)
sr.index = pd.to_datetime(sr.index, unit=self.freq)
sr = sr.between_time('9:30', '16:00',
include_start=True,
include_end=True)
sr = sr.resample('1d').sum()
si = pd.DataFrame(self.sigma_sq_industry)
si.index = pd.to_datetime(si.index, unit=self.freq)
si = si.between_time('9:30', '16:00',
include_start=True,
include_end=True)
si = si.resample('1d').sum()
sf = pd.DataFrame(self.sigma_sq_factor)
sf.index = pd.to_datetime(sf.index, unit=self.freq)
sf = sf.between_time('9:30', '16:00',
include_start=True,
include_end=True)
sf = sf.resample('1d').sum()
return [self.factor_loadings
[docs] @ np.diag(sf[sf.index.date == i].values.flatten())
@ self.factor_loadings.T
+ self.industry_loadings
@ np.diag(si[si.index.date == i].values.flatten())
@ self.industry_loadings.T
+ np.diag(sr[sr.index.date == i].values.flatten())
for i in sf.index.date]
def simulate(self, n_days):
"""
The price process of each stock is continous but sampled at random
times and with Gaussian microstructure noise. Importantly, the
observation times are not synchronous across stocks. Observation times
are restricted to market hours (9:30, 16:00) but the underlying process
continues over night so that there are close-to-open gaps.
Parameters
----------
n_days : int
The number of days of the sample path.
Returns
-------
list of pd.DataFrame
A list with two elements, the prices of each stock in a
pd.DataFrame and the feature of each stock in a pd.DataFrame
with datetime_index.
"""
if self.freq == 'm':
# minutes in day (includes overnight)
n_periods = 24 * 60 * n_days
elif self.freq == 's':
# seconds in day (includes overnight)
n_periods = 24 * 60 * 60 * n_days
else:
raise ValueError("Only frequency ``'s'`` or ``'m'`` supported.")
# generate the n_factors GARCH(1,1) factor processes
self.factor_returns = np.zeros((n_periods, self.factor_loadings.shape[1]))
self.sigma_sq_factor = np.zeros((n_periods, self.factor_loadings.shape[1]))
for i in range(self.n_factors):
self.factor_returns[:, i], self.sigma_sq_factor[:, i] = \
garch_11(n_periods, *self.factor_garch_spec)
# generate the n_ind GARCH(1,1) industry processes
self.industry_returns = np.zeros((n_periods, self.industry_loadings.shape[1]))
self.sigma_sq_industry = np.zeros((n_periods, self.industry_loadings.shape[1]))
for i in range(self.n_ind):
self.industry_returns[:, i], self.sigma_sq_industry[:, i] = \
garch_11(n_periods, *self.industry_garch_spec)
# generate the Gaussian feature process for each stock
self.feature = np.random.normal(
0.,
np.sqrt(self.uncond_var(self.resid_garch_spec)),
self.n_stocks*n_periods
).reshape(n_periods, self.n_stocks)
# generate the residual (idiosyncratic) process for each stock
self.sigma_sq_resid = np.empty((n_periods, self.n_stocks))
self.noise_e = np.empty((n_periods, self.n_stocks))
for i in range(self.n_stocks):
self.noise_e[:, i], self.sigma_sq_resid[:, i] = \
garch_11(n_periods, *self.resid_garch_spec)
# These are the continuous underlying log-returns
self.log_rets = (self.factor_returns @ self.factor_loadings.T
+ self.industry_returns @ self.industry_loadings.T
+ self.feature * self.feature_beta
+ self.noise_e)
# These are the 'continuous' underlying prices.
# Note that the price acquires a drift of size sigma^2_t/2.
self.price = 100 * np.exp(self.log_rets.cumsum(axis=0))
# generate microstructure noise
self.ms_noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, self.price.size).reshape(
self.price.shape[0], self.price.shape[1])
# sample observation times
c = int((1 - self.liquidity) * self.price.size)
self.ms_noise.ravel()[np.random.choice(self.ms_noise.size, c,
replace=False)] = np.nan
# resulting price is non-synchronously sampled with microstructure
# noise, which is scaled by price such that price does not get negative.
# Intuitively, a 1000 dollar stock has a larger (absolute cent) spread then
# 30 dollar stock.
self. price *= (1 + self.gamma * self.ms_noise)
self.cum_feature = self.feature.cumsum(axis=0)
self.price = pd.DataFrame(self.price)
self.cum_feature = pd.DataFrame(self.cum_feature)
self.price.index = pd.to_datetime(self.price.index, unit=self.freq)
self.cum_feature.index = self.price.index
# price is only observable within rmh.
self.price = self.price.between_time('9:30', '16:00',
include_start=True,
include_end=True)
self.cum_feature = self.cum_feature.between_time('9:30', '16:00',
include_start=True,
include_end=True)
[docs]def animate_heatmap(data):
'''
Visualize an evolving series of matrices over time.
This function is useful for visualizing a realization
of conditional covariance matricies from a ``Universe``
simulation.
Parameters
----------
data : list
A list of 2d numpy.ndarrays.
Returns
-------
None
'''
vmin = np.min(data)
vmax = np.max(data)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = sns.heatmap(data[0], vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax,
xticklabels=False, yticklabels=False,)
def init():
plt.clf()
def animate(i):
plt.clf()
ax = sns.heatmap(data[i], vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax,
xticklabels=False, yticklabels=False,)
anim = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate, init_func=init,
frames=np.arange(len(data)),
interval=100, repeat=False)
plt.show()
[docs]def simple(size, corr_matrix, spec, liquidity, gamma):
r"""
Generate a simple p-dimensional GARCH(1,1) log-price process
with microstructure noise and non-synchronous observation times.
Parameters
----------
size : int
The number of 'continous' log-prices.
corr_matrix : numpy.ndarray, shape = (p, p)
The correlation matrix of log-returns.
spec : list
The garch specification.
``[sigma_sq_0, mu, alpha, beta, omega]``
liquidity : float
A value between 0 and 1 that describes liquidity.
A value of 1 means that the probability of observation
is 100% each minute. 0.5 means that there is a 50%
probability of observing a price each minute.
gamma : float >=0
The microstructure noise will be zero-mean Gaussian with variance
$\gamma^2 var(r)$, where $var(r)$ is the variance of the
underlying true return process. This noise is be added to the price.
Returns
-------
price : numpy.ndarray, shape = (size, p)
The p-dimensional price time series.
"""
n, p = size, corr_matrix.shape[0]
log_rets = np.zeros((n, p))
var = np.zeros((n, p))
for i in range(p):
log_rets[:, i], var[:, i] = garch_11(size, *spec)
log_rets = log_rets @ np.linalg.cholesky(corr_matrix).T
# These are the continuous underlying prices. The price
# process acquires the drift term ``var/2`` due to the exponential
# function (rf. SDE of Geometric Brownian Motion)
price = 100 * np.exp((log_rets - var/2).cumsum(axis=0))
# generate microstructure noise
ms_noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, price.size).reshape(
price.shape[0], price.shape[1])
# sample observation times
c = int((1 - liquidity) * price.size)
ms_noise.ravel()[np.random.choice(ms_noise.size, c,
replace=False)] = np.nan
# resulting price is non-synchronously sampled with microstructure
# noise, which is scaled by price such that price does not get negative.
# Intuitively, a 1000 dollar stock has a larger (absolute cent) spread then
# 30 dollar stock.
price *= (1 + gamma * ms_noise)
return price